🤔 Can You Trust a System Without Trusting Anyone?
Blockchain says a resounding YES!
You’ve heard of Bitcoin, the famous cryptocurrency. But Bitcoin, and many other digital currencies, are built on a groundbreaking technology: blockchain.
So, what is blockchain at its core?
It’s a revolutionary way to handle data. It lets people:
- Store, verify, and share information without banks, governments, or middlemen.
- Create permanent records.
- Send money across borders instantly.
- Secure digital information so it can’t be secretly changed. 🚀
This guide will break down how blockchain works for you. You’ll learn its process, what makes it unique, and where it’s used today (and tomorrow!).
Get ready to explore the future of secure information.
📌 Key Takeaways
- ✅ Blockchain is a secure, shared record of data. Think of it as blocks linked together in a chain.
- ✅ It removes the need for central authorities. Trust is built through transparency and clever math.
- ✅ Data, once added, can’t be changed. This makes it perfect for financial and legal systems.
- ✅ Blockchain is already transforming payments, digital identity, supply chains, and much more!
- ✅ It relies on a network of computers (nodes) to verify and store information.
- ✅ Transparency and immutability are its core strengths, making it incredibly robust.
1. What Is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a special kind of database. It stores information in groups called “blocks.” When one block gets full, a new one is created. This new block is then securely linked to the previous one. This creates a “chain” of blocks – that’s where the name comes from! 🏗️
But it’s more than just storage. Blockchain is also a distributed ledger. What does that mean?
- It’s not saved in one single place, like a bank’s server. 🏦
- Instead, it’s shared across many computers, often thousands, all around the world. 🌍
- Every computer in the network (called a “node”) holds a copy of the entire blockchain. When something new happens, like a transaction, all the nodes check it. They agree it’s valid, and then they all update their copy. This ensures everyone sees the exact same version of the data. ✅
Key features that make blockchain stand out:
- ✅ Decentralized: No single company or institution controls it. It’s run by the network itself.
- ✅ Transparent: Anyone can view the transactions on a public blockchain. It’s an open book!
- ✅ Immutable: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed or erased. It’s sealed in forever.
There are also different types of blockchains:
- Public blockchains, like Bitcoin, are open to everyone. Bitcoin is just one famous example of a public blockchain!
- Private and consortium blockchains are more restricted, often used by specific organizations or groups.
2. How Blockchain Works
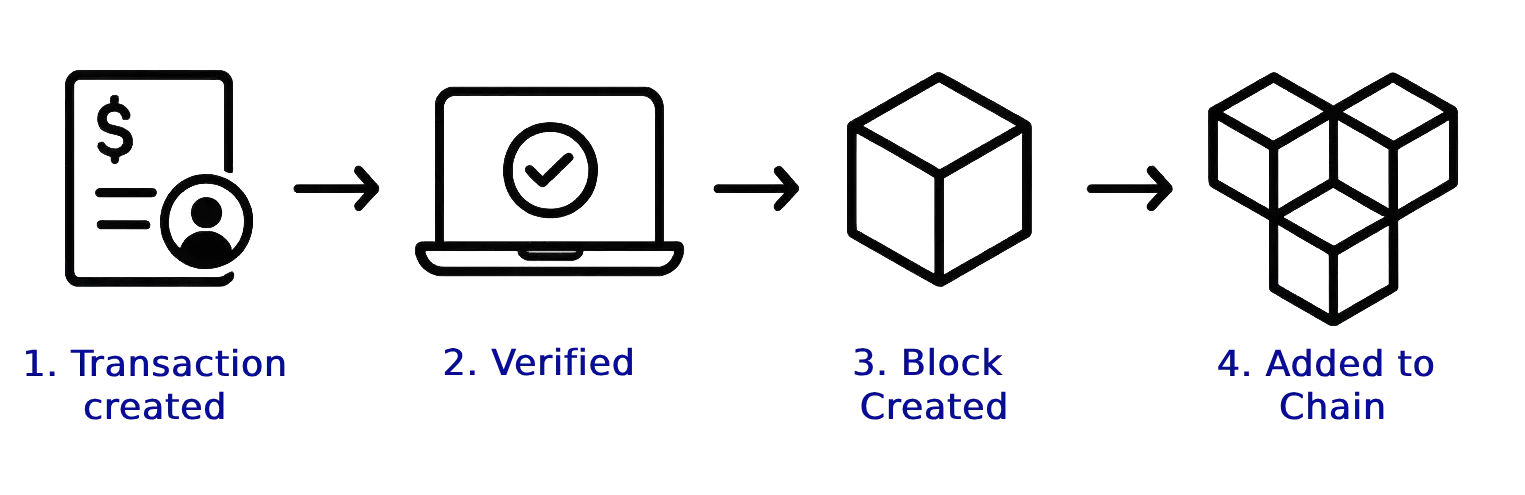
Let’s walk through how blockchain handles a simple transaction. It’s like a digital journey for your data. 🚶♀️
Step 1: Alice Creates a Transaction ✍️
Imagine Alice wants to send 0.5 BTC to Bob. She uses her crypto wallet and enters Bob’s address.
Then, she “signs” the transaction with her unique private key. This signature is digital proof that she owns the coins. It also authorizes the transfer.
Step 2: The Network Checks It 🧐
Once Alice broadcasts her transaction, it quickly reaches thousands of computers (nodes) in the network.
These nodes perform quick checks:
- ✅ Is Alice’s digital signature valid?
- ✅ Does Alice actually have enough Bitcoin to send?
- ✅ Is she trying to send the same coins twice (a “double-spend” attempt)?
If all checks pass, the transaction moves into a “waiting room.” These are valid, but still unconfirmed, transactions. Discover the detailed blockchain transaction process to see how transactions are finalized.
Step 3: The Block Is Formed 🧱
Multiple verified transactions are then grouped together into a new block.
This block isn’t just a list of transactions. It also includes:
- A timestamp (when it was created). ⏰
- A unique code called a hash (like a digital fingerprint for the block). 🧮
- A link to the previous block’s hash. This connection is absolutely crucial!
Here’s why the hash is so important: if anyone tries to change even one tiny detail in one transaction within that block, the block’s hash will completely change.
This “breaks” the link to the next block. It makes the entire chain after it invalid. This is how the system detects tampering instantly! 🚨
Step 4: The Block Is Added to the Chain ⛓️
After the new block is approved, it’s securely attached to the existing blockchain. Approval often happens through a process called “mining” or “staking” – we’ll cover that next!
Every node in the network then updates its copy. At this point, the data inside that block is permanent. It cannot be edited or erased. It’s part of history! 📜
A Quick Look at Consensus Mechanisms: 🤝
To add a new block, the network needs to agree that it’s valid. This agreement is reached through “consensus mechanisms.”
Here are the two most common types:
- Proof of Stake (PoS): This method is more energy-efficient. It involves “stakers” who lock up their cryptocurrency to validate transactions. Instead of competing to solve puzzles, validators are chosen based on how much crypto they “stake” (hold). Every node updates its copy. The data inside is now permanent — and can’t be edited or erased.
- Proof of Work (PoW): This is the famous mechanism used by Bitcoin. In PoW, “miners” compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first one to solve it gets to add the next block and earns a reward. This process secures the network and makes it incredibly difficult to attack.
3. History of Blockchain
The idea of blockchain might seem new, but its roots go back decades. The core concepts behind blockchain have been evolving for a long time. 🕰️
💡 Early Ideas
- In 1991, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta introduced work on a cryptographically secured chain of blocks. Their goal was to create a system that would prevent document tampering.
- They used cryptographic hashes to link blocks of data. This made the data immutable and protected from alteration.
₿ The Rise of Bitcoin
- The real breakthrough came in 2008. An anonymous creator (or group of creators) known as Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper on Bitcoin.
- Bitcoin became the first successful implementation of blockchain. It used this technology to create a decentralized digital currency.
- This solved the “double-spending problem” without needing a central authority.
🚀 The Evolution of Ethereum and Smart Contracts
- In 2015, Ethereum was launched. It took blockchain to a new level.
- Ethereum introduced the concept of smart contracts. These are self-executing programs that run on the blockchain.
- Smart contracts enabled the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and paved the way for DeFi, NFTs, and other innovations.
Since then, blockchain continues to evolve. New networks and applications are constantly emerging. It’s a technology that is continuously shaping our digital future. 🌐
4. Why Blockchain Is So Different
Blockchain completely flips traditional record-keeping on its head. It’s a true game-changer! 🤯
Here’s a quick comparison to show you just how different it is:
| Feature | Traditional System | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Where data is stored | One central server | Shared across thousands of nodes worldwide |
| Who controls it | One company or institution | No single owner – controlled by the network |
| Can it be edited later? | Yes, by admins or insiders | No, data is permanent and unchangeable |
| Can anyone verify it? | Usually not | Yes, fully transparent and verifiable |
| Transaction Speed | Can be slow (days for international transfers) | Can be near-instant (minutes for crypto) ⚡ |
| Transaction Cost | Often high fees (especially for cross-border) | Can be very low, depending on the network |
5. Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain isn’t just for crypto traders anymore! 📈 It’s being used in incredible ways right now, transforming various industries. Here are some real, growing uses today:
Payments 💸
Blockchain lets you send money directly, instantly, and globally. No need for banks or huge fees! For example, sending Bitcoin from the US to a friend in Kenya can take minutes, not days. It’s about financial freedom and efficiency.
Supply Chain 📦
Imagine tracking every single step of a product’s journey. From the farm, to the warehouse, to the store shelf. Companies like IBM and Walmart already use blockchain to track food safety. This brings transparency and trust to complex supply chains. You can know exactly where your food came from! 🍎➡️🛒
Digital Identity 🆔
Tired of dozens of passwords and platforms controlling your personal data? Blockchain lets you truly own your own identity. You could securely sign into websites or apps using your blockchain identity. This gives you back control over your personal information. You decide who sees what! 🔐
Healthcare 🏥
Medical records can be stored privately and securely on a blockchain. They are only shared with the right people, reducing errors and potentially saving lives. Imagine a world where your health data is always safe and accessible only to you and your chosen doctors. ❤️🩹
Voting 🗳️
Digital voting on blockchain can prevent tampering, build trust, and ensure election transparency. This could make elections fairer and more secure for everyone. Every vote would be verifiable and auditable! ✅
Beyond the Basics: Crypto Industry Innovations! 🚀
Since you’re on a crypto site, let’s dive into some more exciting blockchain uses directly from the crypto world:
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): This is a whole new financial system built on blockchain!… It’s finance for everyone, everywhere. 💰 (Start your deep dive with What Is DeFi? A Beginner-Friendly Introduction to Decentralized Finance).💰
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain. They represent ownership of digital art, music, collectibles, and even in-game items. They’ve revolutionized digital ownership and opened up new creative economies. 🖼️🎶
- DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations): DAOs are like companies or communities run by code on a blockchain, without a central leader. Members vote on decisions, making them truly democratic and transparent. It’s a new way to organize and collaborate! 🧑🤝🧑
These are just a few examples. The blockchain space is constantly evolving, with new and exciting applications emerging all the time! Keep exploring!
6. The Future of Blockchain
Blockchain is not standing still; it’s constantly evolving and shaping our digital future.
Here are some key areas where it’s making big waves:
- Web3: The Next Internet: This is about building a decentralized internet. Instead of large companies controlling your data, Web3 gives power back to users. Blockchain is the core technology behind this shift. 🌐
- Metaverses: Virtual Worlds: Blockchain is crucial for metaverses. It allows for true ownership of digital assets (like virtual land or items) and creates secure economies within these immersive online spaces. 🎮
- GameFi: Play-to-Earn Gaming: This combines gaming with finance. Blockchain enables players to own in-game assets as NFTs and earn real cryptocurrency rewards by playing. It’s revolutionizing how gamers interact with their favorite titles. 👾💰
- Scalability Solutions (Layer 2): As blockchain networks grow, they face challenges with speed and cost. Layer 2 solutions are built on top of existing blockchains to process transactions faster and cheaper, making them more efficient for widespread use. ⚡
- Enterprise Blockchain: Beyond public networks, businesses are using private and consortium blockchains for supply chain management, secure data sharing, and internal processes. This brings efficiency and trust to corporate operations. 🏢
The future of blockchain is bright and full of innovation. It promises a more decentralized, transparent, and user-controlled digital world. ✨
To explore cutting-edge research and future directions of blockchain technology, check out this scientific article: An Overview of Blockchain Research and Future Agenda.
7. How Blockchain Builds Trust
In the past, we relied on institutions to verify things. Think of banks, notaries, or government offices. They were the trusted third parties.
Blockchain changes this entirely. It replaces those middlemen with something new:
- Math 🧮
- Code 💻
- Global Agreement 🌍
Here’s how trust is built on blockchain:
- Network Verification: Every piece of information is verified by the entire network. It’s not just one central party checking it.
- Collective Confirmation: All the computers (nodes) in the network work together to confirm its validity.
- Immutability: Once information is added to a block, it’s sealed in forever.
- Transparency: Anyone can check the data.
- Security: No one can secretly change it. This is the power of immutability.
That’s why people say blockchain is “trustless.” This term can be confusing, so let’s clarify what it truly means:
- This doesn’t mean you don’t need trust at all.
- It means you don’t need to trust people or institutions.
- Instead, you trust the underlying system itself: the math, the code, and the collective agreement of the network.
It’s a fundamental shift in how trust is established online. ✨
This paradigm shift empowers individuals and organizations by removing reliance on single points of control, fostering a more robust and resilient digital ecosystem.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
Blockchain can be a complex topic, and it’s natural to have questions! Here are answers to some common inquiries:
Q1: Is blockchain completely private? 🕵️♀️
A: Public blockchains are transparent, showing transactions but not personal names, only wallet addresses. This offers pseudonymity, not full anonymity.
Q2: Can blockchain be hacked? 🛡️
A: Hacking a large blockchain is possible but practically unfeasible due to the immense computing power required. Its decentralized nature makes it incredibly robust. This distributed security model is a cornerstone of blockchain’s integrity.
Q3: Is blockchain just for crypto? 🪙
A: No, absolutely not! While it’s the foundation for cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s uses extend to contracts, ticketing, logistics, digital art (NFTs), and much more.
Q4: What are Smart Contracts? 📜
A: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with terms written directly into blockchain code, automatically executing when conditions are met without intermediaries.
Q5: What’s the difference between blockchain and cryptocurrency? 💡
A: Blockchain is the underlying distributed ledger technology, while cryptocurrency is a digital asset that uses blockchain for secure transactions and ownership.
Q6: Who owns the blockchain? 👑
A: No single entity owns a public blockchain; it’s decentralized and maintained by a network of participants (nodes) globally.
Q7: What is a “node” in blockchain? 💻
A: A node is a computer that connects to the blockchain network, maintains a copy of the ledger, and helps verify and process transactions.
Q8: What are the main challenges for blockchain? 🚧
A: Key challenges include scalability (handling many transactions), regulatory uncertainty, and user adoption, as the technology is still evolving.
Q9: What are the risks associated with blockchain and crypto? ⚠️
A: Risks include market volatility, regulatory changes, potential for scams, and the crucial importance of secure key management to prevent irreversible loss of funds.
🧭 Conclusion
Blockchain is far more than just a tech trend. It’s a fundamental shift in how people share, verify, and protect information online.
Here’s why it’s so impactful:
- Digital Transformation. This technology is profoundly changing how we interact with digital data. 🔄
- Enhanced Trust. It’s building new levels of trust and transparency. 🤝
- Decentralized Control. It achieves this without needing central authorities. 🚫
Even if you never buy cryptocurrency, blockchain will likely shape the tools and services you use every day. Consider how it might impact:
- Future Logins. How you log in in the future, potentially using decentralized identity solutions. 🔐
- Transparent Voting. How you might vote, with more transparent and secure systems. 🗳️
- New Financial Tools. How you’ll manage your money, with new financial tools. 💼
It’s a powerful innovation that continues to evolve and impact our digital world, offering unprecedented opportunities for global collaboration and progress. 🚀
📘 Ready to learn more? Explore our beginner guide: “What Makes Blockchain Secure?”